Study on high moisture extruded pea protein isolate based on acid-induced process : Physicochemical properties, conformational changes and fibrous structure mechanism
Journal article
Sun, Dongyu, Zhang, Bowen, Zhou, Chengyi, Wang, Bo and Wu, Min. (2023). Study on high moisture extruded pea protein isolate based on acid-induced process : Physicochemical properties, conformational changes and fibrous structure mechanism. Food Hydrocolloids. 141, p. Article 108746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.108746
| Authors | Sun, Dongyu, Zhang, Bowen, Zhou, Chengyi, Wang, Bo and Wu, Min |
|---|---|
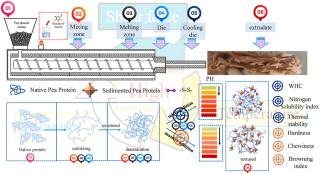
| Abstract | The present study aims to gain a better understanding of the physicochemical properties and quality attribute changes, and fibrous structure formation mechanisms of pea protein analogs with different glucan-δ-lactone (GDL) additions under high moisture extrusion. The results showed that the pH value of the extrudates gradually approached the isoelectric point and the zeta potential increased with the increase in GDL, which reduced the water holding capacity, nitrogen solubility index and browning index values, while increasing the hardness, chewiness and fibrous degree of the extrudates. The comparison revealed the maximum zeta potential value and total SH, and minimum free SH of the raw material, suggesting the unfolding and cross-linking of proteins under the triple action of the extruder. The relative content of β-sheet as the predominant component of protein extrudate decreased, while α-helix increased, and λmax was bathochromiclly shifted through FTIR and fluorescence spectroscopy. However, negative trends were observed when the GDL concentration reached 1%, due to the excessive concentration of the GDL accelerating the aggregation and sedimentation of proteins, and intensified the phase separation degree in the cooling die during the extrusion process, thus promoting the change in the velocity gradient. In addition, the thermal stability of the extrudate first increased and then decreased as the GDL concentration increased, and showed a three-step thermal degradation stage. The pores and highly irregular fibrous filaments transformed into a highly compact and coarse matrix with an excessive GDL concentration, as observed by SEM. These findings validate the potential of GDL to improve the textural attributes and structure formation of meat analogs, and provide a reference for the development of acid-induced proteins under high moisture extrusion. |
| Keywords | extrusion; meat analogues; pea protein; glucono-δ-lactone; physicochemical properties |
| Year | 2023 |
| Journal | Food Hydrocolloids |
| Journal citation | 141, p. Article 108746 |
| Publisher | Elsevier Ltd |
| ISSN | 0268-005X |
| Digital Object Identifier (DOI) | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2023.108746 |
| Scopus EID | 2-s2.0-85152273066 |
| Page range | 1-10 |
| Funder | National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) |
| Natural Science Foundation of Beijing Municipality | |
| Publisher's version | License All rights reserved File Access Level Controlled |
| Output status | Published |
| Publication dates | |
| Online | 11 Apr 2023 |
| Publication process dates | |
| Accepted | 02 Apr 2023 |
| Deposited | 23 Jun 2023 |
| Supplemental file | License All rights reserved File Access Level Open |
| Grant ID | 32171912 |
| 6232018 |
https://acuresearchbank.acu.edu.au/item/8z2yy/study-on-high-moisture-extruded-pea-protein-isolate-based-on-acid-induced-process-physicochemical-properties-conformational-changes-and-fibrous-structure-mechanism
Download files
Supplemental file
| Sun_2023_Study_on_high_moisture_extruded_pea_[GRAPHICAL_ABSTRACT].jpg | |
| License: All rights reserved | |
| File access level: Open | |
Restricted files
Publisher's version
444
total views302
total downloads13
views this month6
downloads this month